Short-Dated Products: Reducing Unsalable Returns and Supply Chain Waste
The glut of soon-to-expire products within the pharmaceutical supply chain is a costly problem impacting multiple stakeholders, but smart technology and innovative inventory management systems offer cost-saving solutions.
A Guide to Immune Globulin Billing and Reimbursement

Reimbursement for expensive immune globulin (IG) therapies can be challenging and frustrating for providers. Here’s a guide to help ensure they are reimbursed for the cost of these medications.
Complying with Rules Ensures Reimbursement for Drugs

Healthcare costs continue to rise and payment models subsequently evolve, payers nevertheless largely decide which expensive high-investment drugs will be reimbursed and under what circumstances.
Secondary Antibody Deficiency
Demand for IG products has doubled, going from 3 million grams just a decade ago to 7 million grams year-over-year today. What is to account for this increase?
Opioid Dependence in Infants: A Growing Crisis
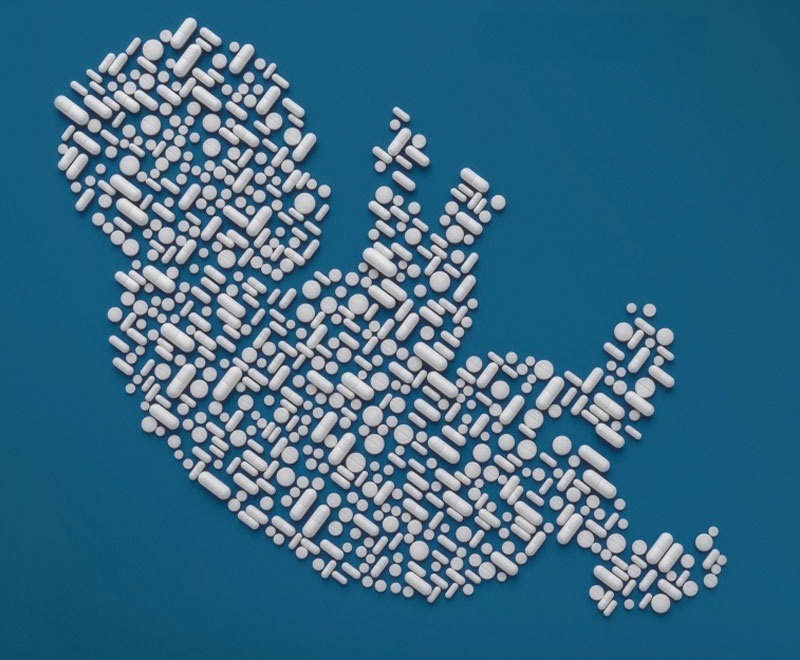

One baby born every hour dependent on opiate drugs; treatment is difficult, and health impacts can be lifelong.
The Growing Need for Supportive Care in Oncology
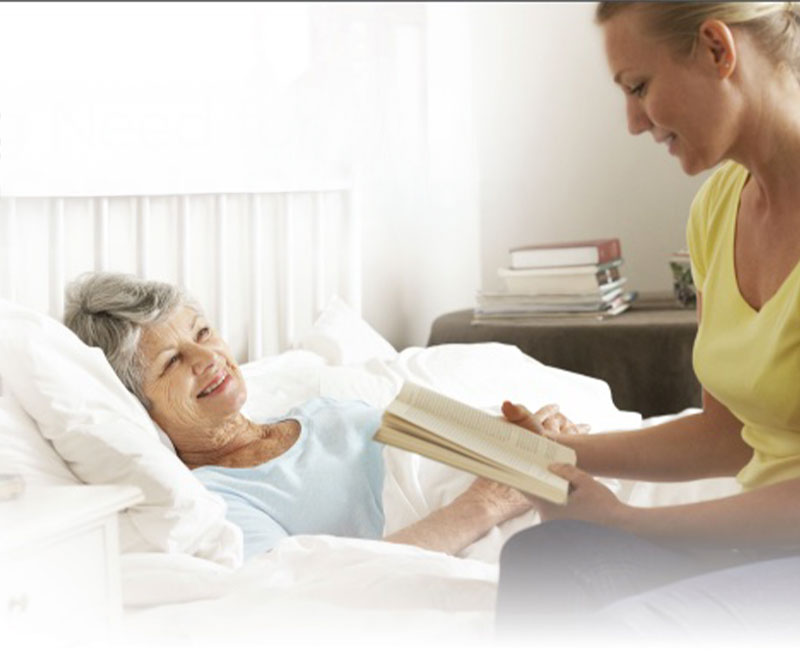

As baby boomers age, rates of cancer diagnosis and survival increase, causing an increasing need for supportive oncology care.
Myths and Facts: Shingles
Knowing the facts about shingles can help you to better protect yourself against it — and how to treat it if you get it.
Update on Toxic Shock Syndrome
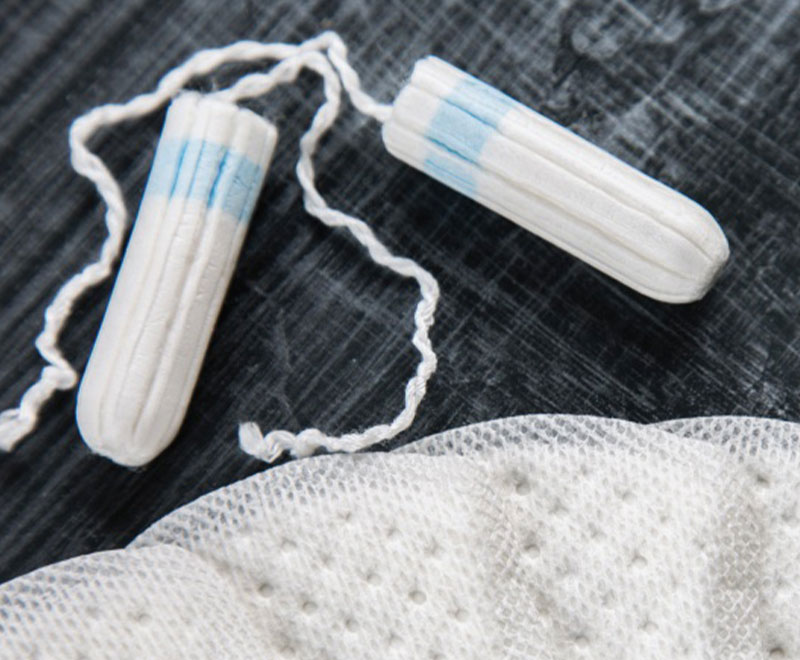

Toxic shock syndrome remains a serious, life-threatening complication of certain types of infections that can be fatal.
Nutrigenomics: How Genes and Nutrition Interact
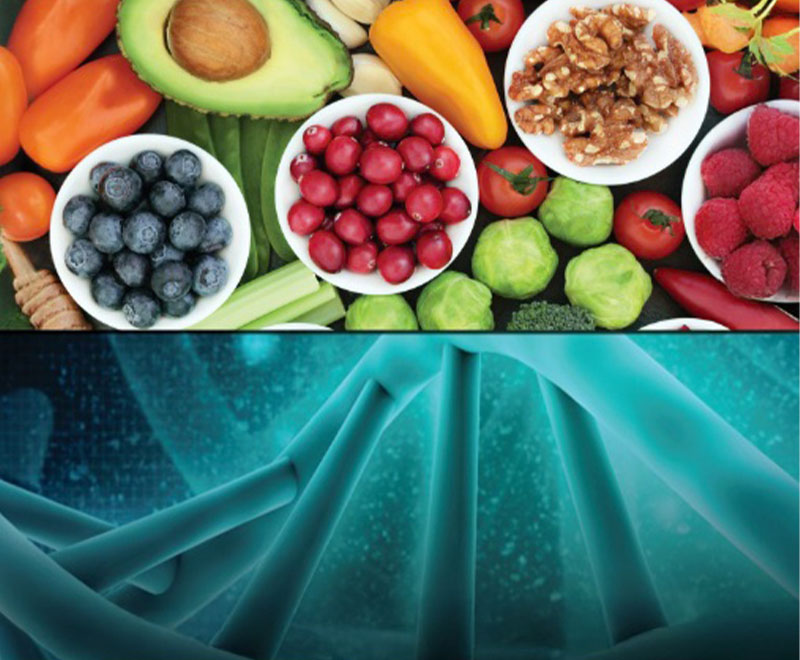

Using nutrition to benefit health through the care and feeding of genes, though still in its infancy, is an exciting field of study seeing exponential growth.
Stopping Alzheimer’s with a Preventative Vaccine?

Despite the many vaccine candidates undergoing clinical trials, experts doubt an effective vaccine for Alzheimer’s disease is on the horizon.