Industry Insight
Information, Observation & Analysis
Therapeutics Articles
This revolutionary technology shows promise for addressing a myriad of challenges in medicine, but ethical dilemmas remain.
Known as liquid gold, human plasma is proving to be a valuable ally in the fight against cancer.
While still in their early stages of research, FDA has approved more than a dozen complement inhibitors to treat various conditions, and there is hope that more will be on the horizon to treat others.
Therapeutic plasma exchange may improve outcomes for patients diagnosed with sepsis or septic shock, but funding is needed to conduct needed clinical trials.
Misconceptions about GLP-1 drugs could interfere with patients' efforts to achieve their weight-loss goals.
Since the approval of BabyBIG, the only treatment for this rare but life-threatening disease affecting infants mostly under 6 months, the mortality rate is now less than 15 percent.
Though mostly eradicated in the U.S., treatment for rabies must begin immediately with hyperimmune globulin and vaccines.
With 16 FVIII products now approved for the treatment of hemophilia A, many patients with this disease are now able to live a normal life.
With almost a quarter of women receiving inadequate prenatal care in the U.S., more needs to be done to inform women about the myths surrounding this essential healthcare service.
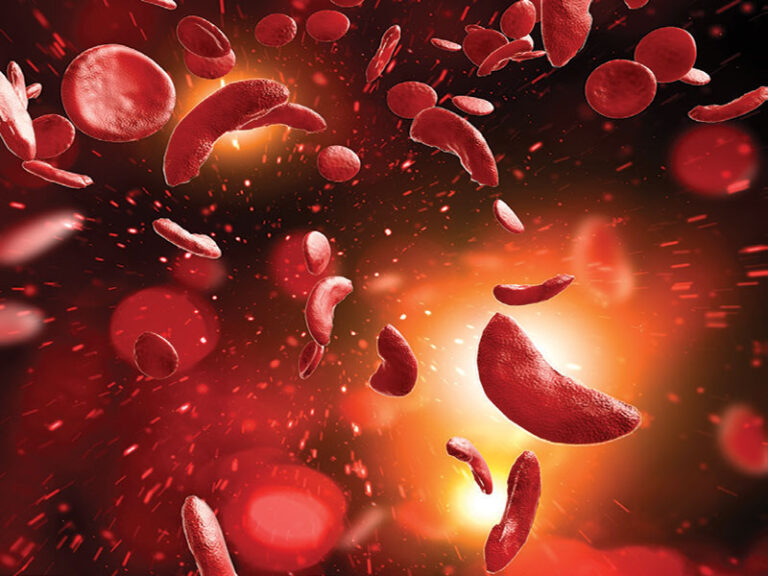
Affecting more than 100,000 American children and adults, sickle cell disease is an inherited hemoglobinopathy that results when a single-nucleotide mutation in the ß-globin gene yields an abnormal “sickle” hemoglobin (HbS). Now, these patients may be eligible for a one-time gene therapy that offers the potential of a durable functional cure by eliminating severe VOCs and associated hospitalizations.
Touted as a more natural approach to hormone replacement therapy, this plant-based anti-aging remedy has evolved from an unregulated safety concern to a mainstay of modern medicine.
Menopause is a normal, natural event in every woman’s life, but it can cause a variety of uncomfortable symptoms. New therapies show promise for bringing relief and an improved quality of life.