Industry Insight
Information, Observation & Analysis
Therapeutics Articles
Renewed interest and research in psychedelic compounds is giving formerly illicit drugs a 21st century image makeover. Are they really breakthrough solutions for treatment-resistant conditions such as depression and PTSD? At this point, the data looks promising.
For decades, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has defied the best efforts of vaccine makers to bring it to heel, until now.
This growing field of intervention-based therapeutics promises to enhance patient health and make healthcare more proactive.
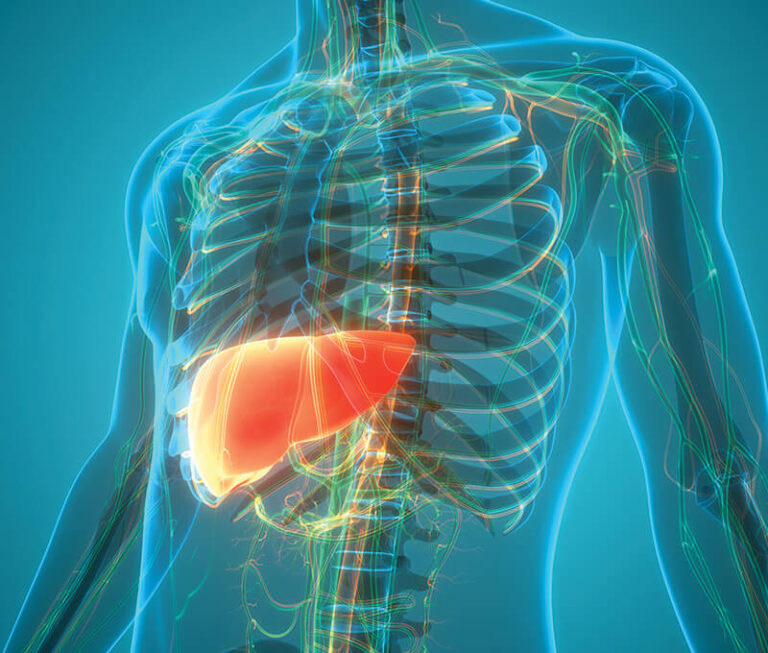
The shortcomings of AAT augmentation therapy for AATD are currently the targets of a diverse range of new investigational therapies.
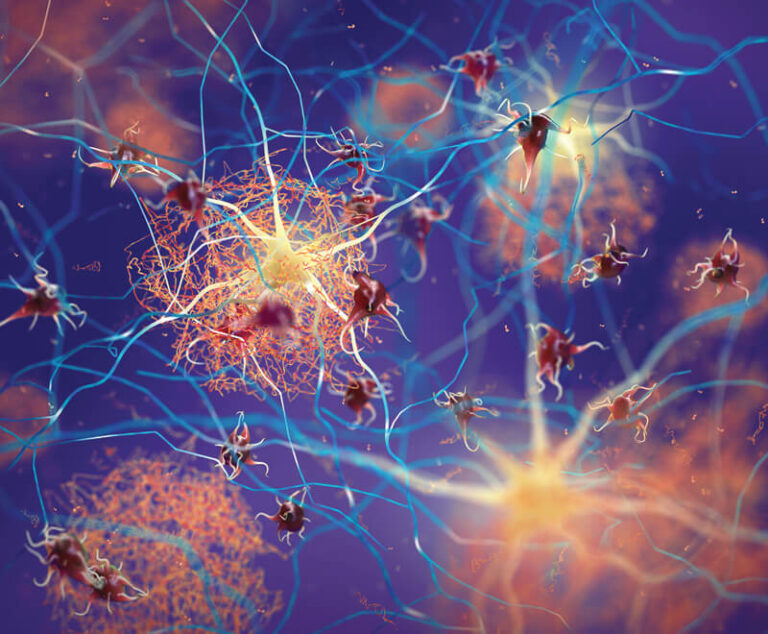
While a cure for Alzheimer’s remains elusive, new diagnostic tools and treatment options are improving patient quality of life.
Exciting new developments in gene therapy and genome editing show promise for treating a variety of genetic diseases.
RSV infections account for a large share of U.S. hospitalizations for lower respiratory tract disease due in large part to a lack of immunization and prophylactic therapies, but new developments and cutting-edge therapies may soon become standard medical practice.
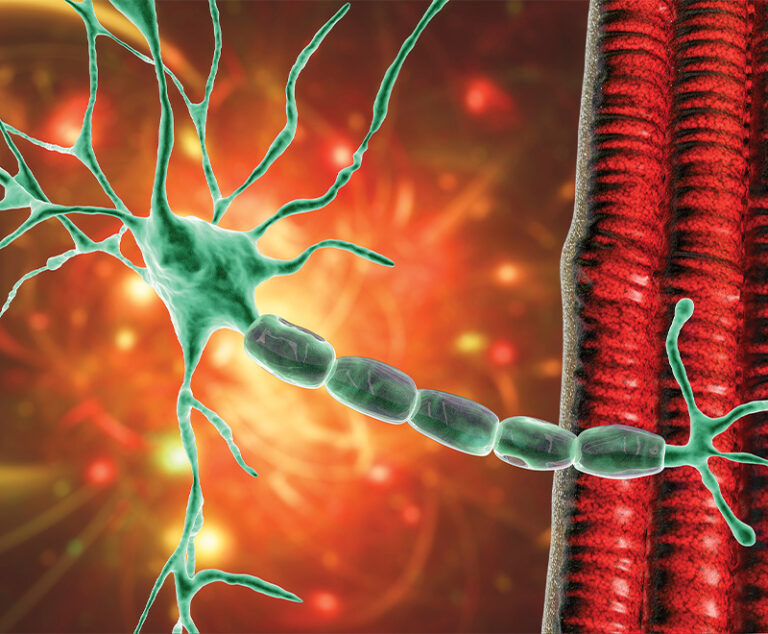
While acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, corticosteroids and thymectomy are generally considered first-line therapies for MG, many patients additionally require proven immunosuppressive therapies (ISTs) such as azathioprine, cyclosporine/tacrolimus or mycophenolate mofetil, or immunomodulatory therapies, including intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) or plasma exchange (PLEX).
Understanding the factors contributing to the current shortage of immune globulin could help to address a crisis that threatens dire consequences for patients.
Will genetic testing and whole genome sequencing become part of the standard of care in treating patients?
Newly created treatments for high-risk COVID-19 patients have proved highly effective. Unfortunately, challenges with their distribution and administration have limited their use.
The decades-old dream is to correct the factor deficiency through a single infusion of a hemophilia gene therapy that produces steady high protective levels of FVIII or FIX.