Scientists Design Nanoparticle for Safer and More Effective Vaccine Delivery
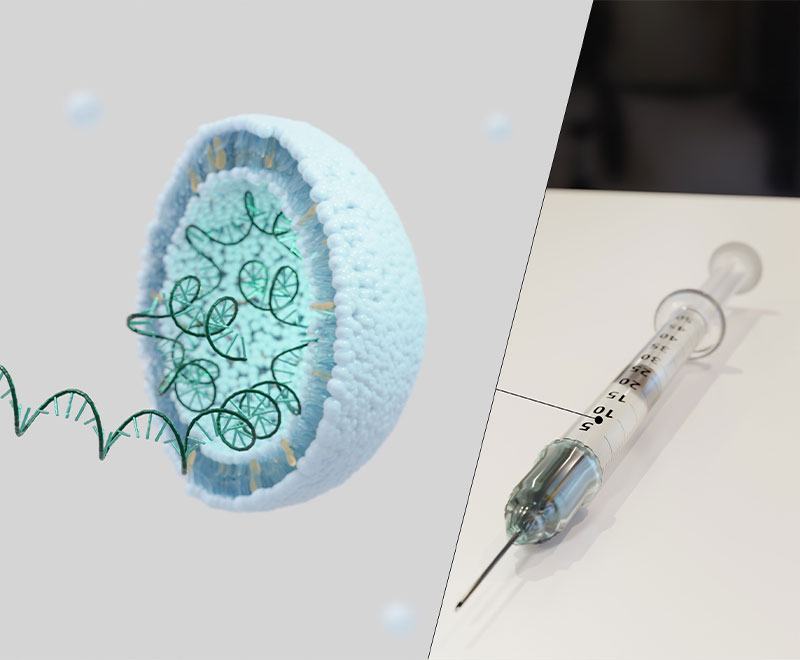
Engineers at MIT have designed anew type of nanoparticle that could safely and effectively deliver vaccines for diseases such as HIV and malaria.
Higher SCIG Dosing Results in Lower Infection Rate and Fewer Missed School/Work Days

Treatment with a higher dose of subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) correlates with reduced risk of infection and fewer missed school or work days in patients with primary humoral immunodeficiency (PI), according to findings from separate U.S. andEuropean trials of CSL Behring’s Hizentra 20% SCIG product.
Study Helps to Explain IG Distribution in the Body
SL Behring has developed a pharmacokinetic model that shows how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes and eliminates immunoglobulin following subcutaneous administration.
Prophylaxis Prevents Bleeds and Arthropathy in Children with Hemophilia A (the ESPRIT Study)

A multinational European research team has reported findings from a randomized controlled trial that compared the efficacy of prophylaxis with episodic (on-demand) therapy in children with severe hemophilia over a 10-year time period.
Gene Therapy Successful in Treating Immune Disease

Several recent studies have proven gene therapy is successful in treating immune diseases.
Autoimmune Skin Disease Is Associated with Neurologic Disease
A new study suggests that individuals with the autoimmune skin disease bullous pemphigoid appear more likely to have a diagnosis of neurologic disease.
Prenatal Flu Vaccine May Prevent Flu in Infants
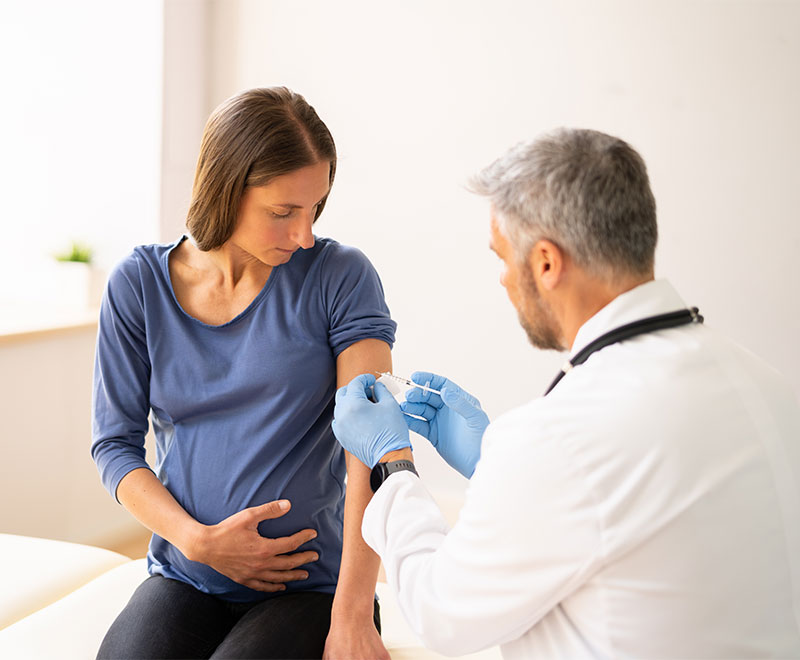
A new study suggests prenatal use of influenza vaccine may protect young infants against the flu.
Blood Test May Diagnose Alzheimer’s
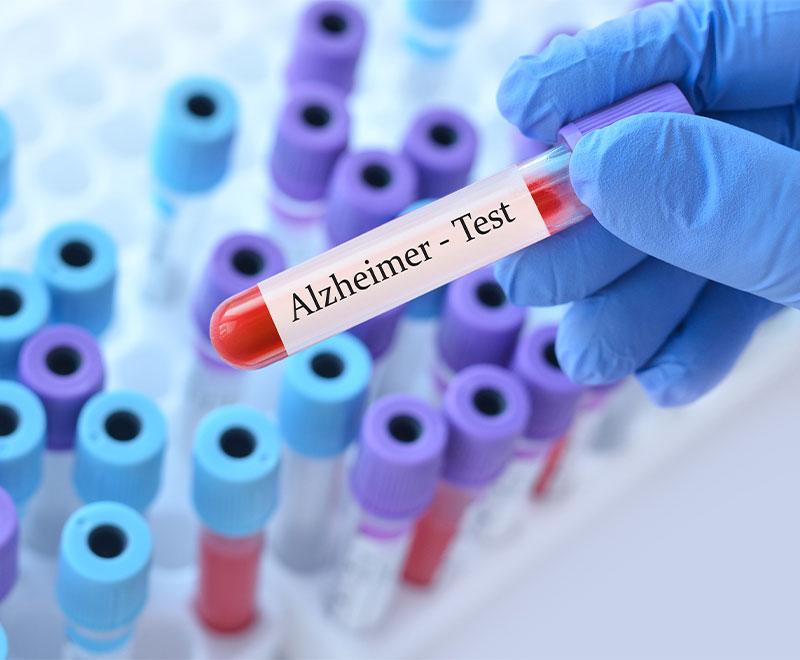
A blood test for antibodies produced in the immune system may potentially be used in the future to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease in its early stage.
Immune Modulation Therapy May Treat Ovarian Cancer

Researchers from the Royal Women’s Hospital and Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, are testing immune modulation therapy to treat ovarian cancer.
Human Albumin Reduces Endothelial Dysfunction; Improves Survival in Mouse Model of Sepsis

French investigators found that infusion of human serum albumin formulated at a 4% concentration significantly improved survival time in Swiss mice injected with lipopolysaccharide endotoxin, while 20% human albumin and normal saline provided no protective benefit.